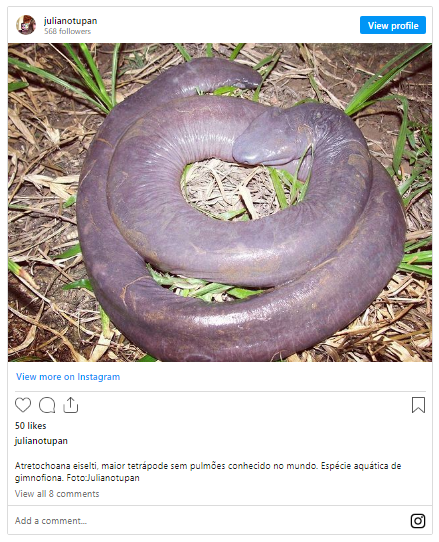
‘Man-aconda’ stuns the world: Unveiling the astonishing tale of the eye-striking phenomenon
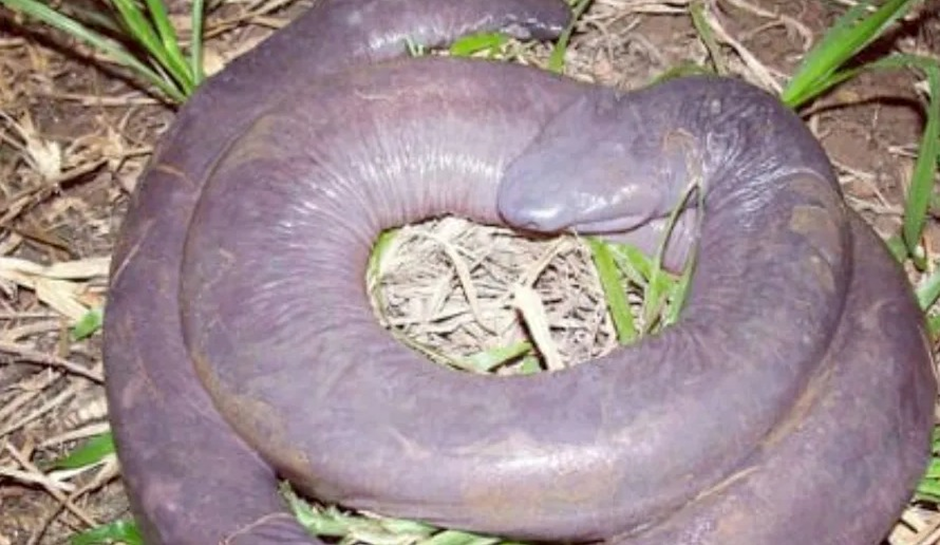

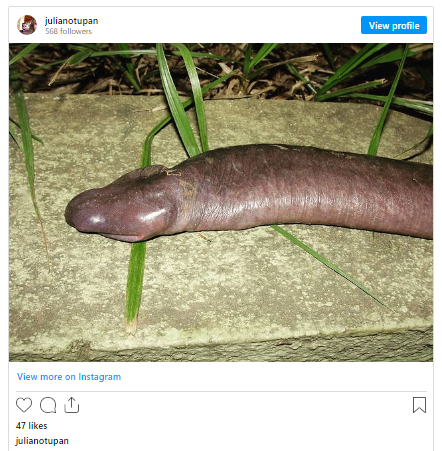
The Amazon Rainforest, often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth,” spans over 6.7 million square kilometers and harbors an astonishing diversity of plant and animal species. Within this vast expanse of lush greenery lies the intricate network of rivers and tributaries that sustain a myriad of aquatic life forms, including the elusive man-aconda. Nestled amidst the submerged vegetation and muddy riverbeds, the man-aconda finds its habitat in the murky depths of the Amazon River basin.
The Amazon River, the largest river in the world by discharge volume, serves as the lifeblood of the rainforest, providing essential nutrients and sustenance to countless organisms. It is within this dynamic aquatic environment that the man-aconda thrives, utilizing its unique adaptations to navigate the labyrinthine waterways and hunt for prey.
Despite its intimidating appearance, the man-aconda plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance of its habitat. As an apex predator, it helps regulate the population of smaller aquatic organisms, thereby preventing unchecked growth that could destabilize the fragile ecosystem. By preying on fish, amphibians, and invertebrates, the man-aconda contributes to the intricate web of life in the Amazon River, shaping the dynamics of predator-prey interactions and nutrient cycling.
The behavior of the man-aconda offers fascinating insights into its evolutionary adaptations and ecological niche. While much of its behavior remains shrouded in mystery, scientists have observed specific patterns and traits that provide clues to its lifestyle. For instance, the man-aconda is primarily nocturnal, preferring to hunt under the cover of darkness when its prey is less vigilant. It employs stealth and ambush tactics, relying on its elongated body and powerful jaws to capture and consume unsuspecting prey.
One of the most intriguing aspects of the man-aconda’s biology is its unique reproductive strategy. Unlike most amphibians, which lay eggs, female man-acondas give birth to live young, a phenomenon known as viviparity. This reproductive mode, rare among amphibians, offers distinct advantages in the challenging aquatic environment of the Amazon River. By giving birth to fully formed offspring, the man-aconda ensures the survival of its progeny in the face of predation and environmental hazards.
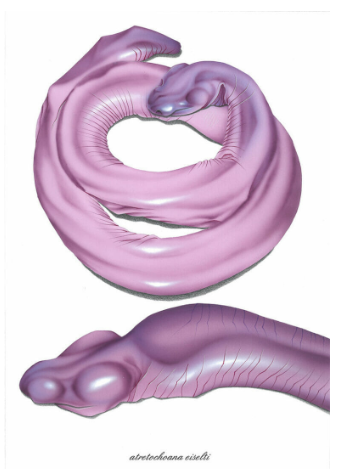
The evolutionary origins of the man-aconda provide further insights into its place in the natural world. Molecular studies have revealed that the man-aconda belongs to the family Typhlonectidae, a group of limbless amphibians known as caecilians. Caecilians are among the least studied vertebrates, with many species still awaiting discovery and classification. The man-aconda’s elongated body and reduced eyes suggest adaptations to its subterranean lifestyle, where it navigates through dark, watery tunnels in search of prey.
Despite its ecological importance, the man-aconda faces numerous threats to its survival, primarily due to habitat destruction and human activities in the Amazon region. Deforestation, land degradation, and pollution pose significant challenges to the man-aconda’s habitat, leading to habitat loss and fragmentation. Additionally, illegal wildlife trade and overexploitation further endanger the man-aconda’s population, pushing it toward the brink of extinction.
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting the man-aconda and its habitat are essential for ensuring its long-term survival. Collaborative initiatives involving governments, NGOs, and local communities are crucial for implementing sustainable land management practices and establishing protected areas where man-acondas and other threatened species can thrive. Public awareness and education play a vital role in fostering appreciation for the unique biodiversity of the Amazon Rainforest and the importance of its conservation.
In conclusion, the man-aconda represents a fascinating example of the diversity and complexity of life in the Amazon Rainforest. Through scientific research, conservation action, and public engagement, we can unlock the mysteries of this enigmatic creature and secure a sustainable future for the Amazon ecosystem. By working together to protect the man-aconda and its habitat, we can ensure that future generations will continue to marvel at the wonders of the natural world.